The last twenty years have been an era of digital renaissance, where the Internet has become not just a tool but a part of our daily lives. We pay bills, communicate, shop, and manage our finances using online services and electronic payment systems. But along with the many benefits, there are also threats, among which phishing occupies a special place.
Phishing is more than just a word. It’s a clever strategy used by fraudsters to steal confidential information, mainly by spoofing and luring users. And, unfortunately, this is a fairly common type of attack.
According to statistics, 96% of phishing attacks are carried out via email. Attackers send emails that look like well-known services or organizations and try to get confidential information from us, such as passwords or credit card numbers. Another 3% of attacks are carried out through malicious websites that can cause irreparable damage to our devices and data. And only 1% of phishing attacks are carried out via phone calls, but that doesn’t mean this method is any less dangerous.
Therefore, it is important to understand the nature of these attacks and take timely measures to protect your privacy and security online.
Read the article to find out:
- What is Internet phishing
- How Internet phishing works
- How to protect yourself from phishing
- In conclusion, what’s next?
- Questions and answers about Internet phishing
What is Internet phishing?
Let’s take a closer look at the phenomenon of online phishing.
Phishing, as the word itself indicates, is a type of online fraud that involves stealing confidential user data. It is not just a scam, but a cunning strategy where attackers provoke people to disclose their personal information, such as phone numbers, bank cards, logins, and passwords.
The scheme is simple: fraudsters offer users various “attractive” opportunities or services that appeal to the target audience. For example, they may promise to find out who has viewed their social media profiles, even though the platform itself does not provide such functionality. Or they can offer a product at an incredible discount to attract online customers.
There are many ways that attackers can use this strategy. They can hide their intentions behind attractive pretexts: checking authorization on a website,unsubscribingfrom spam emails, providing special offers, or even installing new applications.
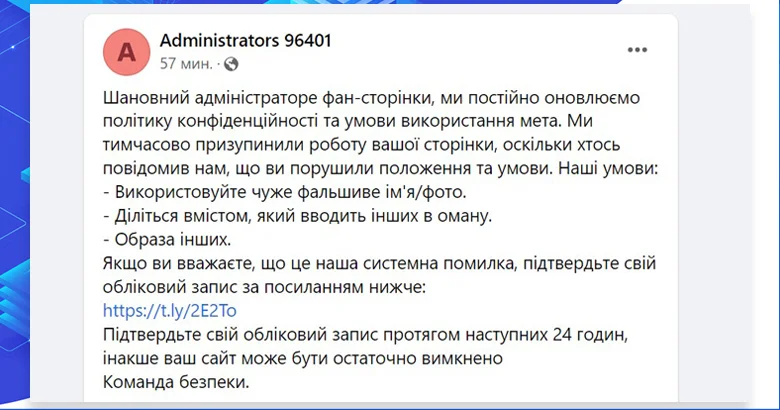
How Internet phishing works
Let’s take a look at how online phishing works and why it is so effective. Phishing differs from other types of fraud in that its victim actually provides their confidential data voluntarily. This is achieved through the skillful use of various tools, such as phishing sites, email newsletters, data capture pages, pop-ups, and targeted advertising.
The scenario is usually the following: a user receives an attractive offer or invitation to register for some benefit, or to confirm their personal data, if it concerns, for example, banking or commercial institutions with which they interact. Attackers usually masquerade as well-known companies, social networks, or email services, sending emails on behalf of these organizations. For example, in order to appear to be an online retailer, fraudsters use addresses similar to Aliexpress or Aliexxpress.
Attackers often rely on the low level of cybersecurity awareness among users. Their main goal is personal data that gives them access to financial resources. Thus, not only individuals, but also banks, electronic payment systems and other institutions with significant financial potential can become victims.
Examples of Internet phishing schemes
Online phishing schemes may seem complex, but they are actually simple but effective methods of deception used by attackers to steal personal information and financial data. Let’s take a look at some of the most common examples that can threaten your online security:
- Phishing emails: This old but still effective method involves sending you an email that pretends to be an important message from your bank, social media company, or other source. You will usually be asked to confirm your details, such as your username and password, sometimes even your bank card numbers. Remember, no reputable resource will ever ask you to share this sensitive information over email.
- Interception of email responses: This type of phishing exploits vulnerabilities in the email protocol to intercept your responses to phishing emails. When you reply to an email, it can be automatically forwarded to the attackers, who can then try to squeeze even more information or mislead you.
- Phishing on online auctions: Attackers can use legitimate online auctions to sell illegally obtained goods. They may appear to be honest sellers, but in reality receive money through fake web platforms, bypassing official payment systems.
- Fictitious charitable organizations: This scheme takes advantage of your willingness to help others. Scammers may send you an email or contact you via social media, asking for donations for fictitious charitable projects or to help the sick. Before making any donations, do some additional research to make sure it’s a genuine organization.
- Phishing online stores: Fraudsters can create look-alike online stores that offer products at very low prices or with big discounts. However, this is often just a sneaky way to get your financial information. Before making purchases online, check the reliability of the store and its reputation.
Be aware of these phishing schemes and stay cautious online. Your personal information and safety should always come first.
How to recognize phishing: Fraudsters’ tricks and how to avoid them
When people receive an email about winning some kind of raffle or lottery, they usually feel happy and look forward to their prize. But an unexpected victory can hide a trap. Very often, criminals use this trick, hoping for our naivety and desire to get something for free.
It is important to remember that emails about winnings may not be what they seem. They usually come from unknown or suspicious senders, and at first glance, they may raise doubts. If you have never needed an answer to the question “How did I get into this lottery?“, it is probably phishing.
Some attackers go further, trying to convince you to log in to suspicious websites to claim your “prize“. They can create phishing online stores that look like absolutely authentic resources. By asking you to enter personal data for “verification” or “authorization“, they are really just trying to steal your identity and money.
How to recognize these traps? First, pay attention to the website URL. It can often be similar to the official address of a resource you know, but with some differences. For example, it may contain misspellings or additional characters.
Secondly, carefully check any links in emails or messages. Clicking on them usually takes you to suspicious or phishing sites. If you are required to log in or enter confidential information on such a site, it is better to refuse to do so.
Also, be careful with email senders. Check their address and sender information. Do you know this email? Does it match the official contacts of the company or organization in question?
Another way to recognize phishing attacks is to carefully review all the information you are asked to enter. Attackers may try to collect your personal data, including credit card numbers, passwords, and other sensitive information. Do not give them this opportunity.
You should always be vigilant and cautious online. Phishing attacks can take many forms, but with the right knowledge and caution, you can avoid them and protect your data.
Sources of audience attraction to phishing sites
In search of new ways to attract audiences to phishing sites, fraudsters are constantly improving their methods. Their sources of user acquisition are diverse and sophisticated. One of the most common methods is sending personal messages, where fraudsters try to convince their potential victims of winning or other favorable conditions. Another method is email spam, where attackers send mass messages with offers or tempting deals.
No less effective are advertising campaigns that attract users’ attention through interesting content or incentives. Usually, such ads are disguised as real products or services, but the link leads to a phishing site. In addition, fraudsters can use images that demonstrate the functionality of applications or services, and leave comments under them with links to phishing resources. This strategy, known as “padding,” creates the impression of reliability and the propensity to use real people.
Once users land on a phishing site, fraudsters try to retain them as much as possible and involve them in the fraudulent scheme. This can be achieved through mergers and informational materials that give the impression of legitimacy and security. Thus, the scheme works as follows: “Source -> Padding ->Phishing landing page”, where each step has its own important role in attracting and deceiving the target audience.
How to protect yourself from phishing
When it comes to protecting yourself from phishing, there are a few simple but effective online security rules to follow.
The most important thing is to never disclose confidential data, even if someone really insists. No bank or social network will ever ask you to do so via email.
Get a good antivirus with an updated database. Modern programs of this type are able to detect spyware and malware, as well as warn you about suspicious sites. Do not ignore their warnings – they can save you from trouble.
Pay attention to the design of the sites you visit. If they look sloppy or suspicious, they may be phishing sites.
Check the address bar in your browser. Even minor changes may indicate that you have landed on a phishing site. Be careful of shortened links as well.
When accessing banking websites, make sure that the connection is protected by the HTTPS protocol. The display of a padlock in the address bar is a good sign.
Be on the lookout for emails that call for immediate action or evoke an emotional reaction. They are often fraudulent.
Do not use public Wi-Fi to access your bank accounts. They may not be secure and your data may be intercepted.
If you notice any phishing attempts, report them to the appropriate authorities. By doing so, you will help not only yourself but also other users avoid problems.
And most importantly, don’t take risks by clicking on questionable links. Even if they come from your friends, it can be a trap. Be careful online, and your data will be safe.
In conclusion, what’s next?
In conclusion, I recommend that you familiarize yourself with the other articles contained in the attached materials below. Additional analysis and increasing your expertise in this area will help you become even more secure in the big world of the Internet.
- What is a website
- What is a data center?
- What is a web host? How does it work
- How to create a WordPress website in 2024
- How to edit domain DNS records in cPanel
And don’t forget that our team is always ready to answer your questions and provide additional support via live chat on our website. Take care and be safe online!
Questions and answers about Internet phishing
Internet phishing is a type of fraud where attackers try to obtain personal information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, through fake websites or emails.
Phishing sites often have an unusual design, misspellings, or an incorrect URL. It is best to check the address bar and establish a secure connection (HTTPS).
Phishers can request passwords, credit card numbers, personal data, social security numbers, and other sensitive information.
The consequences of phishing can include loss of personal information, financial loss, identity theft and other forms of fraud
Protecting yourself from phishing includes being alert to suspicious messages and links, installing anti-virus software, and regularly updating your passwords.
Responding to suspicious emails can confirm your activity to the attacker and intensify attack attempts.
Phishing attacks occur regularly and can target any Internet user.
Checking links before clicking helps you avoid potentially dangerous websites and phishing attacks.
Regular internet security training, using two-factor authentication, and installing spam blocking software can help protect you from phishing attacks.
If you are a victim of a phishing attack, immediately change your passwords, contact your bank or other known services that may be affected, and report the incident to law enforcement.



